Top 21 Important CNC Lathe Accessories every Machinist should Know
The CNC lathe accessories provide your operations with enhanced precision and efficiency and superior safety standards during machining.
These tools enhance workholding while streamlining toolholding alongside automation and maintenance to deliver normalised machine operations with minimal downtime and exceptional quality outcomes.
Let’s look at some common accessories you will find in lathe machines.
Workholding Accessories
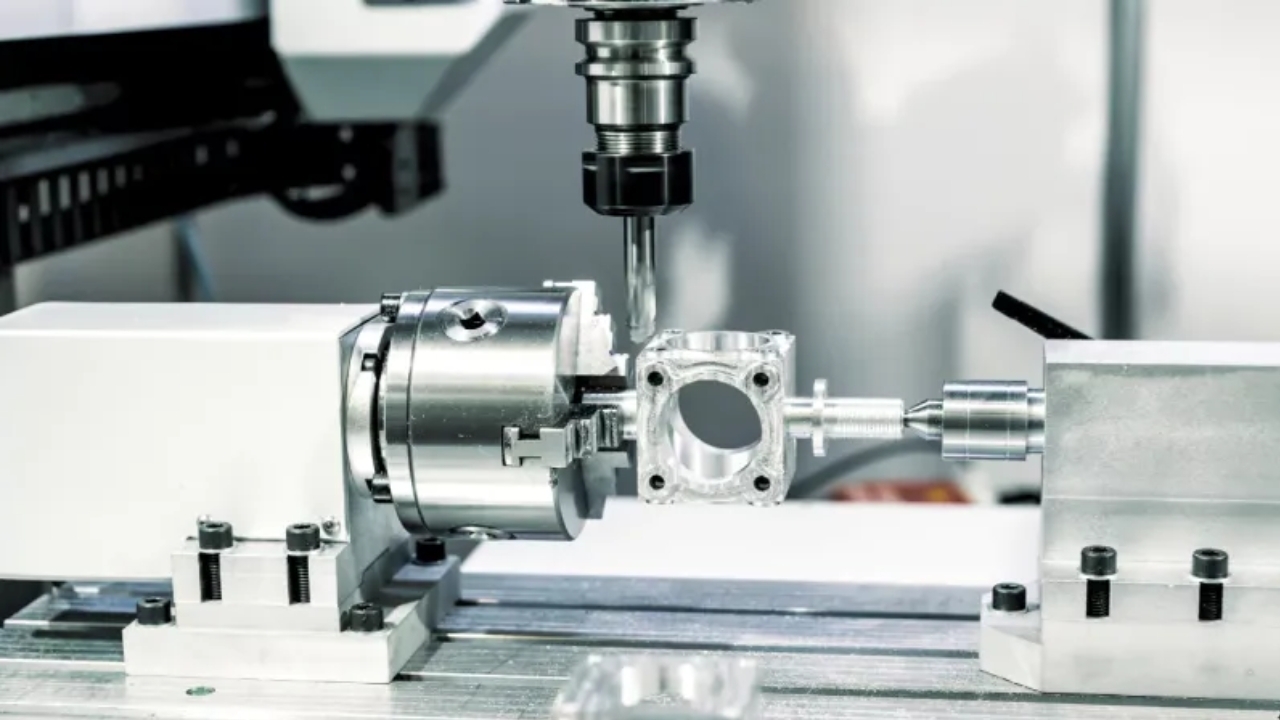
1. Chucks (3-jaw, 4-jaw, collet chucks)
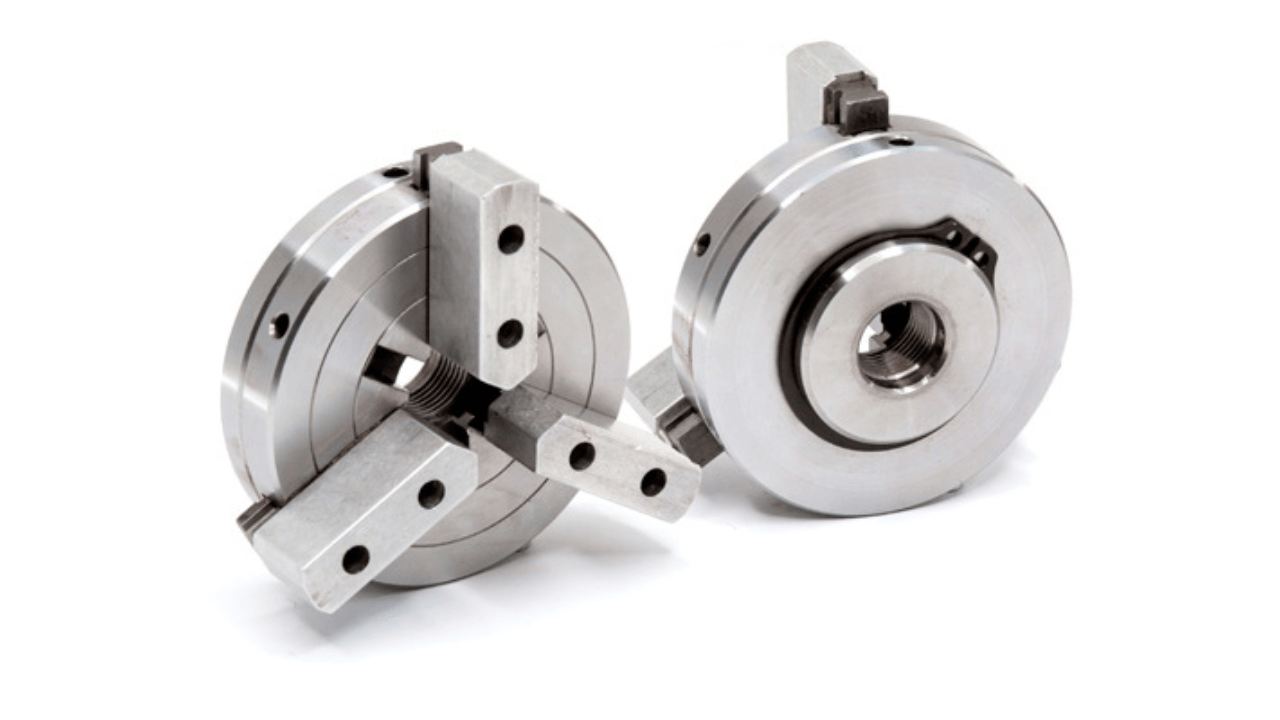
The CNC lathe uses chucks as a means to grip workpieces with complete stability during operation. The 3-jaw chuck offers immediate centring when you work with round or hexagonal stock, while the 4-jaw chuck provides individual adjustment for different-shaped materials. The precision of collet chucks, along with their ability to grip small parts securely, leads to reduced vibration for improved high-accuracy machining.
2. Faceplates

Large or irregularly shaped workpieces require faceplates for secure attachment when they cannot fit into a chuck. The surface creates a reliable holding point that lets you apply clamps for workpieces or additional securing components. Better control over off-centremachining becomes possible combined with reduced risks of slippage during cutting operations.
3. Steady Rests and Follow Rests
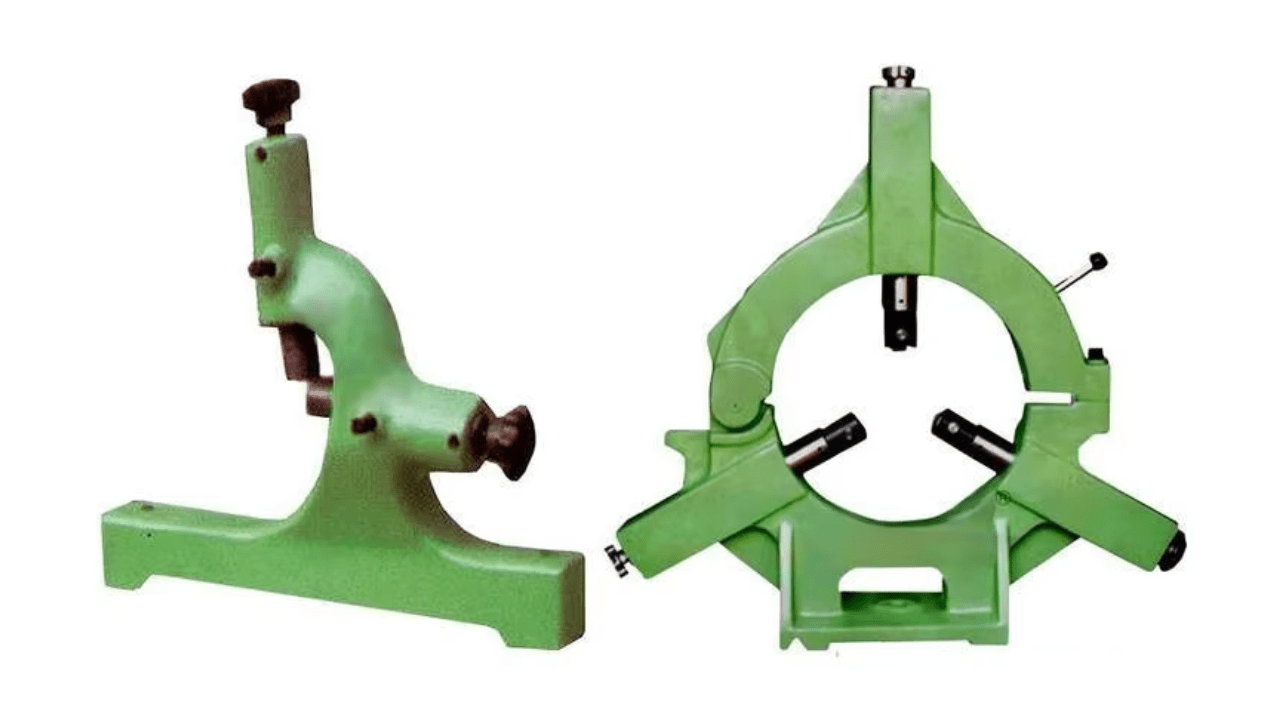
Steady rests help you support long workpieces, and so they stay stable for accurate machining. Follow rests travel along with the cutting tool to provide machine stability and minimise vibrations known as chatter. The accessories provide essential support that helps prevent materials from bending as they encounter cutting forces, particularly when dealing with thin, flexible materials.
4. Mandrels and Centres
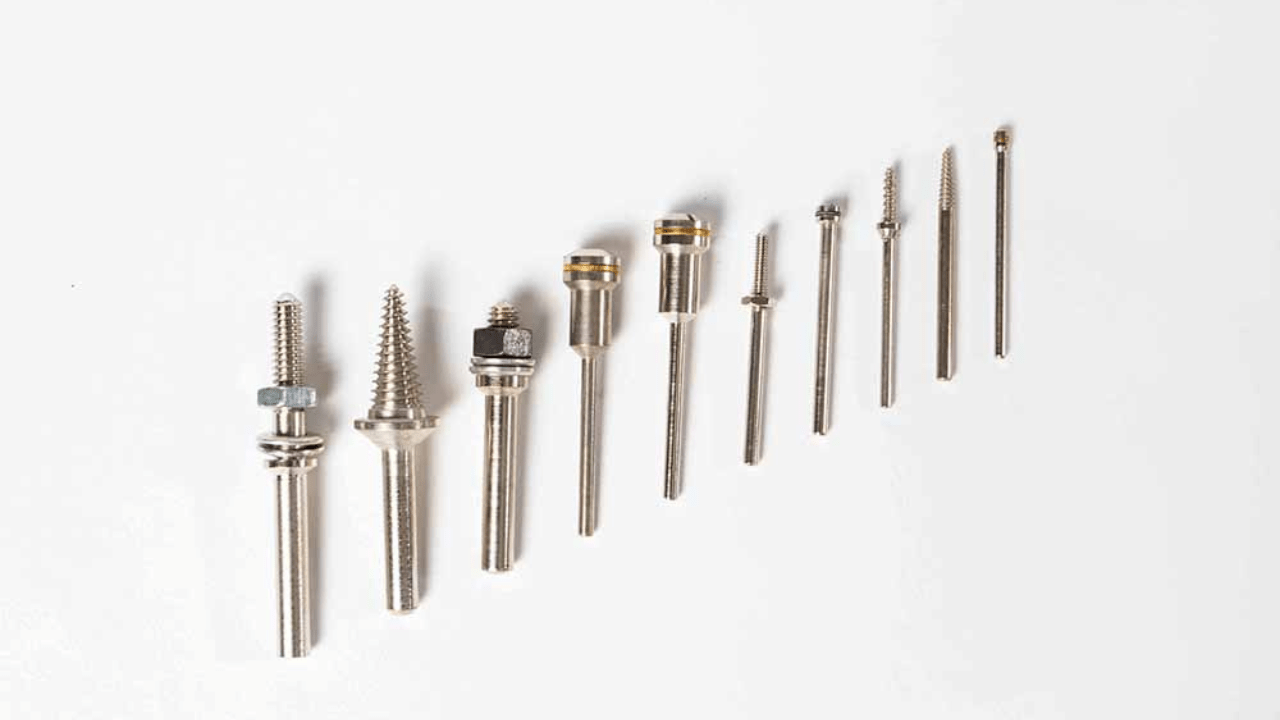

Mandrels act as tools that provide a firm grip of hollow or thin-walled workpieces by using their ability to expand inside the bore. Live and dead centres function as supports for workpieces through their respective mechanisms, which minimise runout. The tools serve to enhance precision levels so they become vital for machining operations on cylindrical parts such as shafts and pipes.
Toolholding Accessories
5. Tool Turrets
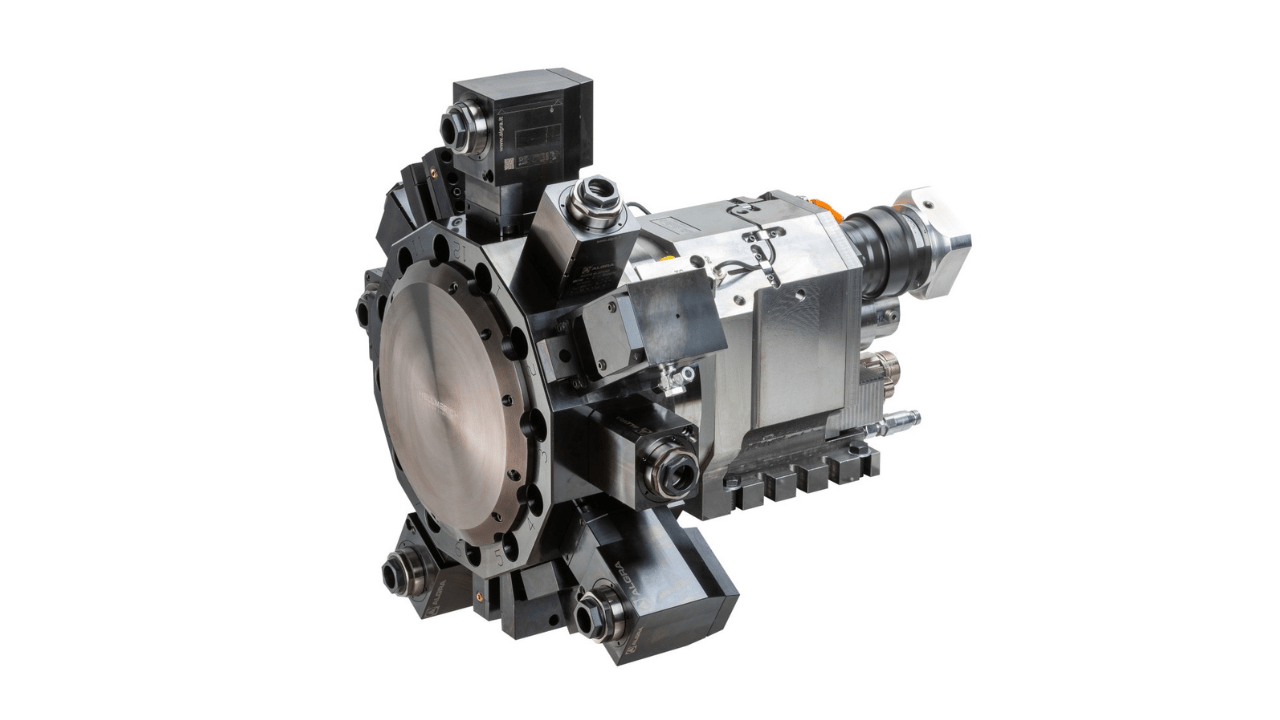
Tool turrets provide a system where you can keep several cutting tools which automatically switch during the machining process. The programming of tool positions creates more efficient workflows while minimising equipment standstill time. The automated operation of turrets enables simultaneous turning, drilling and threading with minimal operator involvement to deliver both speedier cycle times and reliable accuracy.
6. Quick-Change Tool Posts
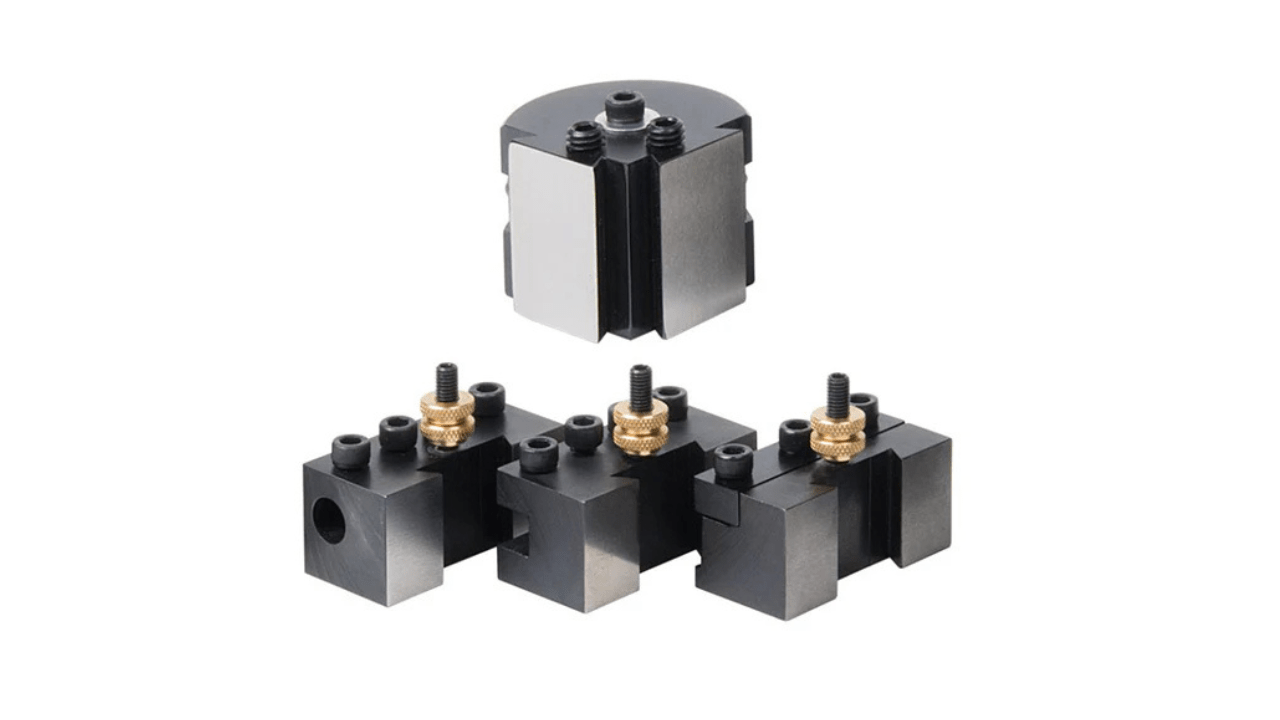

Quick-change tool posts allow you to quickly change tools without having to realign them. Using these preset holders means that the tools are always positioned consistently. It reduces setup time, hence increases productivity and ensures accuracy.
With this system, you can easily switch from operations like face turning and grooving, extending your overall machining flexibility.
7. Boring Bars and Holders
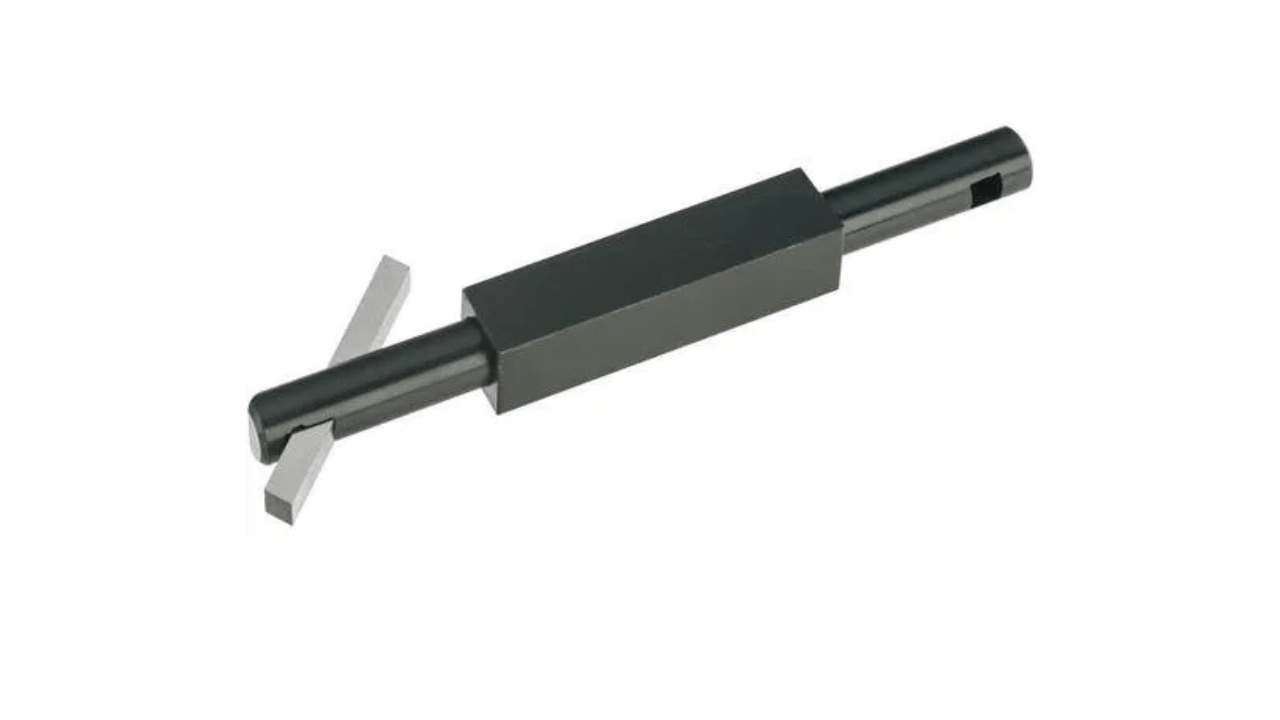
Your boring bars and holders use boring bars and holders to enlarge existing holes with precision. It holds the boring bar, so it is secured and stable and reduces vibration. Selecting the right combination of cutter and lead gets your hole diameters accurate and finishes smooth. Internal machining, such as boring cylinders and bearing seats, requires these tools.
8. Live and Dead Centres
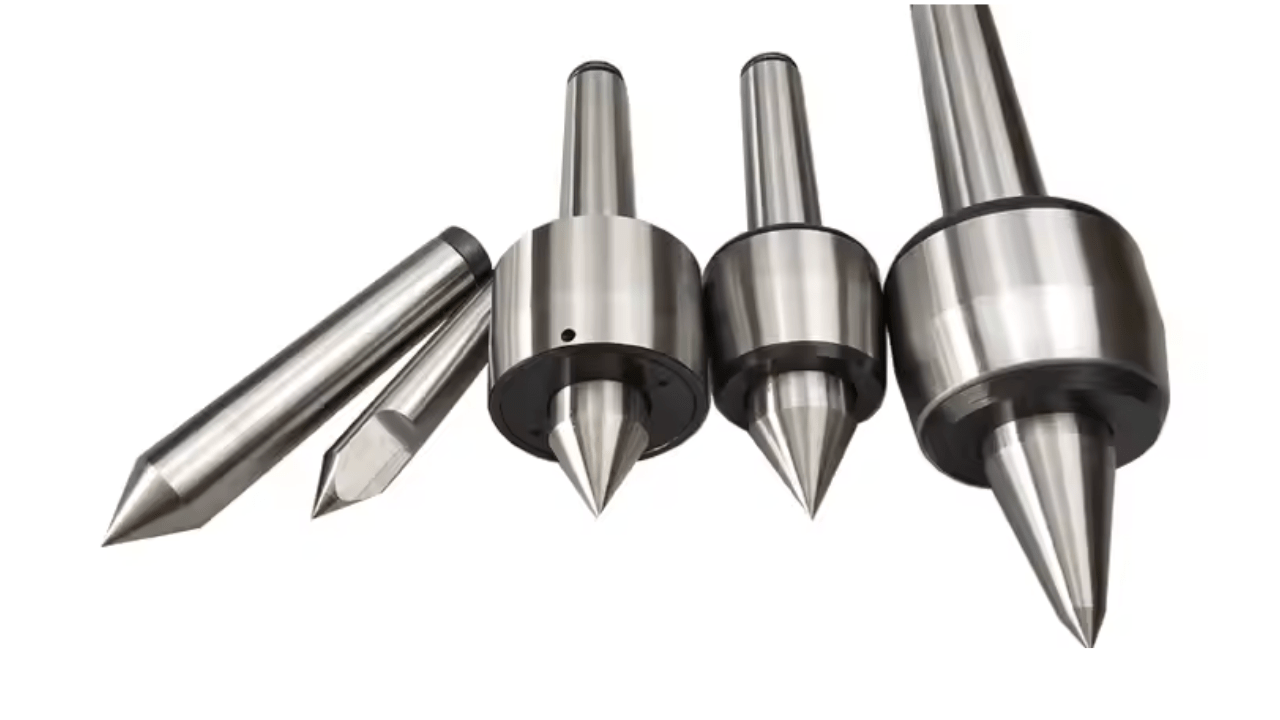

To stabilise workpieces during machining, you use live and dead centres. Friction and heat buildup are reduced by having a live centre rotate with the workpiece. This rigid support is given by a dead centre which remains stationary.
Both allow you to reduce runout, and therefore less runout leads to higher precision when machining shafts, rods or long component parts.
Cutting and Measurement Tools
9. Carbide Inserts and Tool Bits
For accurate cutting, shaping, and finishing, you use carbide inserts and tool bits. Durability and longer edge life than with steel are achieved with carbide inserts. Turning, facing, and grooving are functions that require versatility, and tool bits provide it.
This means you can get a better surface finish and increase machining efficiency by choosing the correct insert or bit.
10. Threading Tools
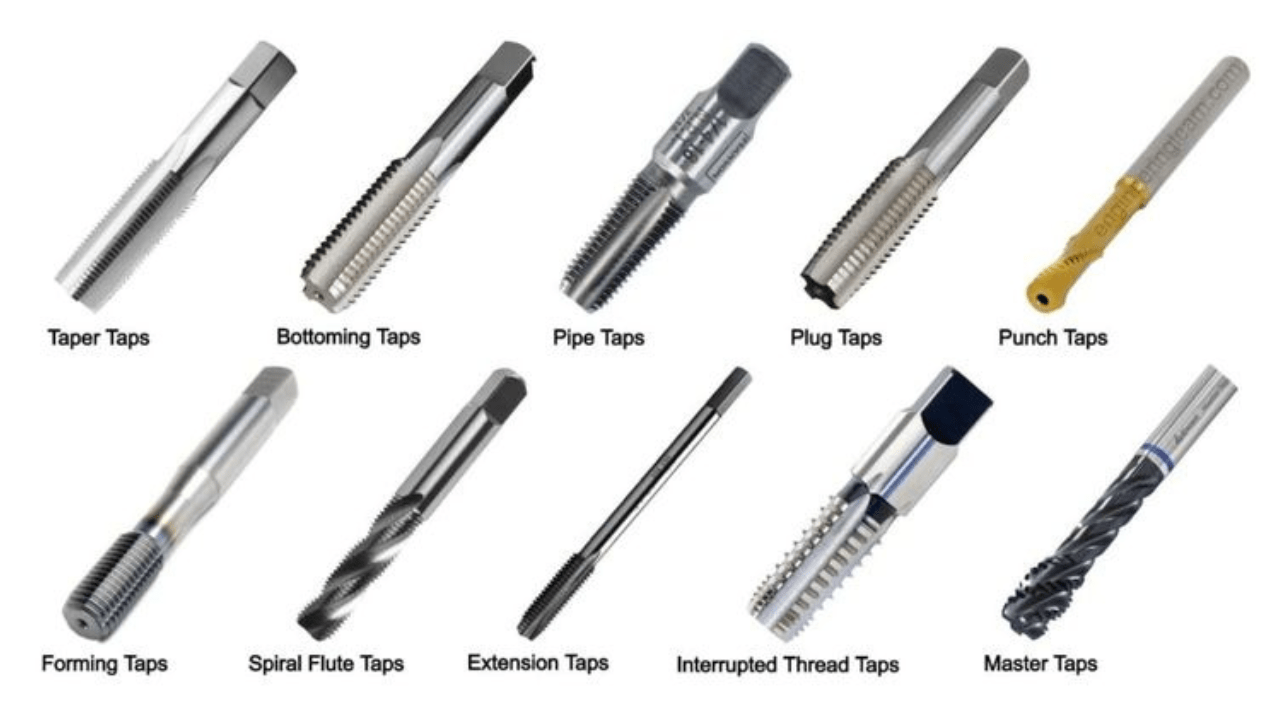

When you rely on threading tools to cut precise internal and external threads on workpieces. Threading inserts, taps, and dies assure that bolts, nuts, and fasteners are properly fitted. This keeps assembly easier and create a consistent thread profile, but it will also ensure secure connections in the machined components.
11. Boring Tools
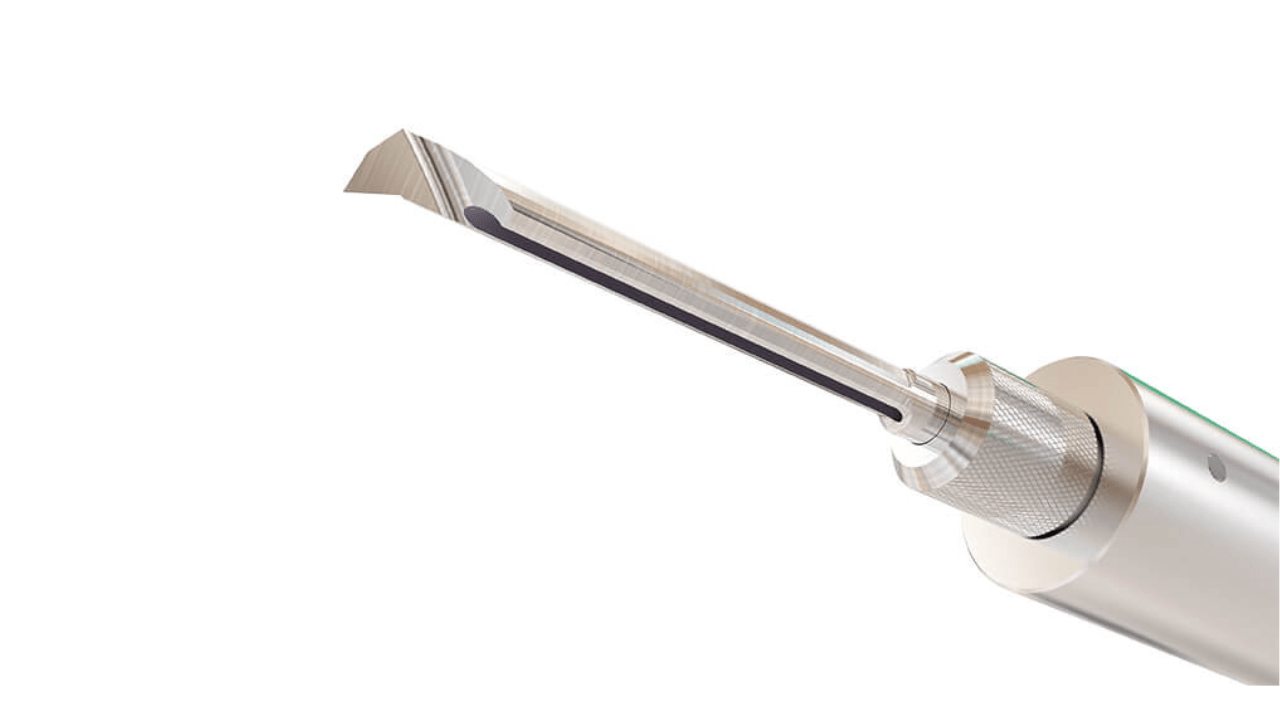

Precision is applied when you use boring tools to refine or enlarge existing holes. The cutting insert is held in place with a boring bar, guaranteeing stability and accuracy. By using the proper boring tool, you can obtain tight tolerances and smooth finishes suitable for the milling of engine cylinders, bearing housings, and precision pipe fittings.
12. Dial Indicators and Micrometres
Using dial indicators and micrometres, you measure dimensions accurately. Runout, alignment, and deflection are checked by a dial indicator to keep the machining as precise as possible. Thickness and diameter measurements are provided by a micrometre. Using these tools keeps you at your high-quality standards, limiting errors and the parts fitting in assemblies the way they are supposed to.
Coolant and Lubrication Systems
13. Coolant Pumps and Nozzles
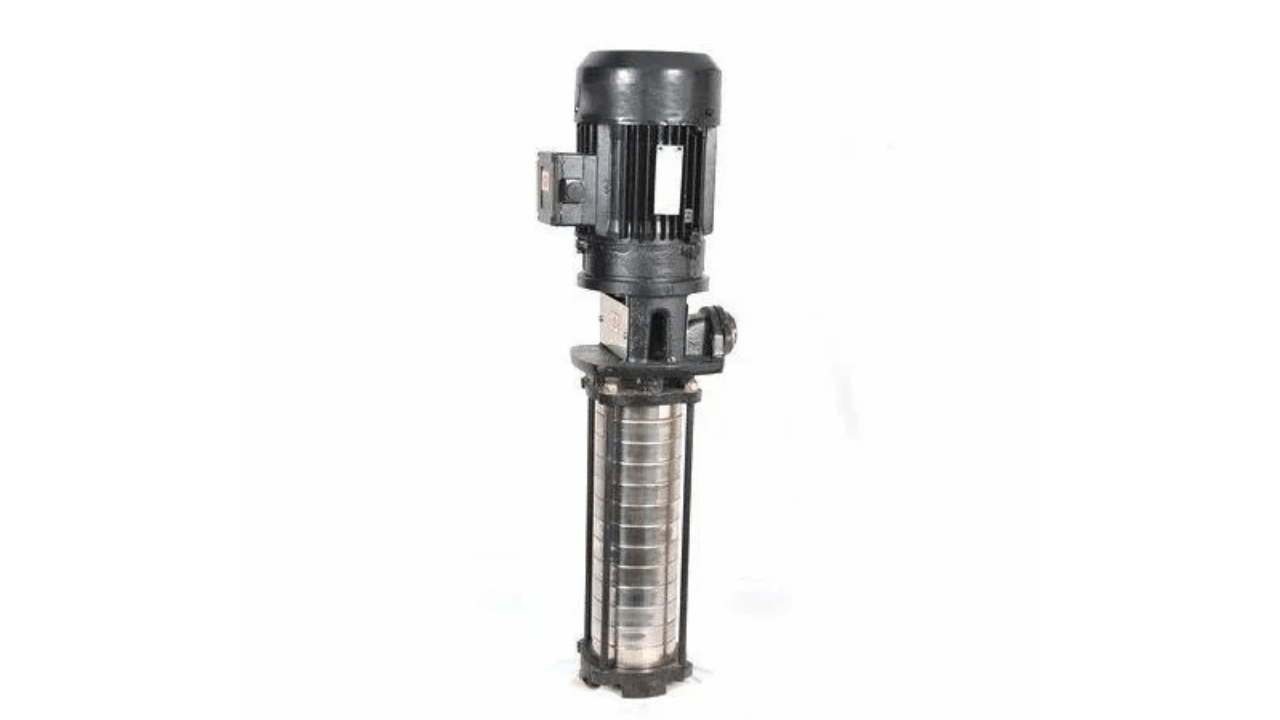

You cool the cutting area by directing coolant against it, using coolant pumps and nozzles to do so. The pump provides a steady flow with adjustable nozzles for precise cooling. The system will prevent overheating, improve surface finishes, and flush out chips for efficient and accurate machining.
14. Mist Collectors
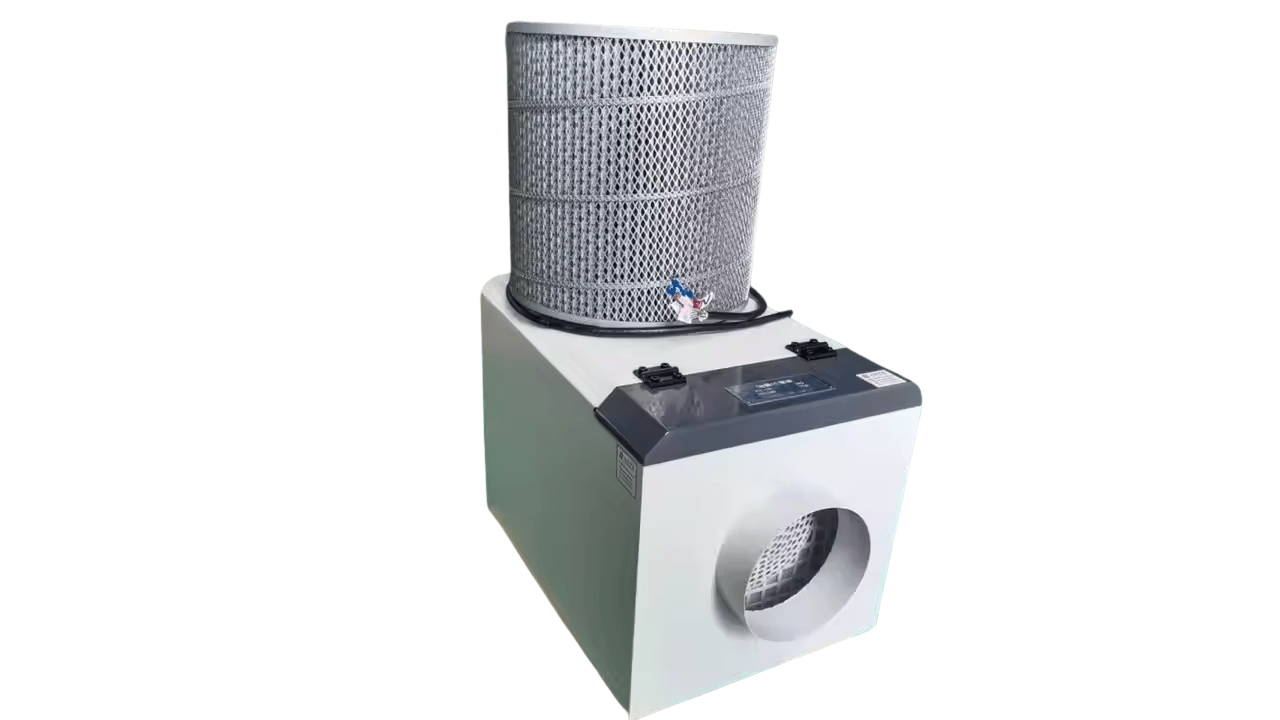

You use mist collectors to catch airborne oil and coolant mist from the workspace. By filtering harmful particles, these devices ensure a good quality of air and well-maintained air quality. It also carries with it a reduced potential for unhealthy working practices, reduced machine contamination, and compliance with workplace safety regulations.
15. Chip Conveyors and Trays
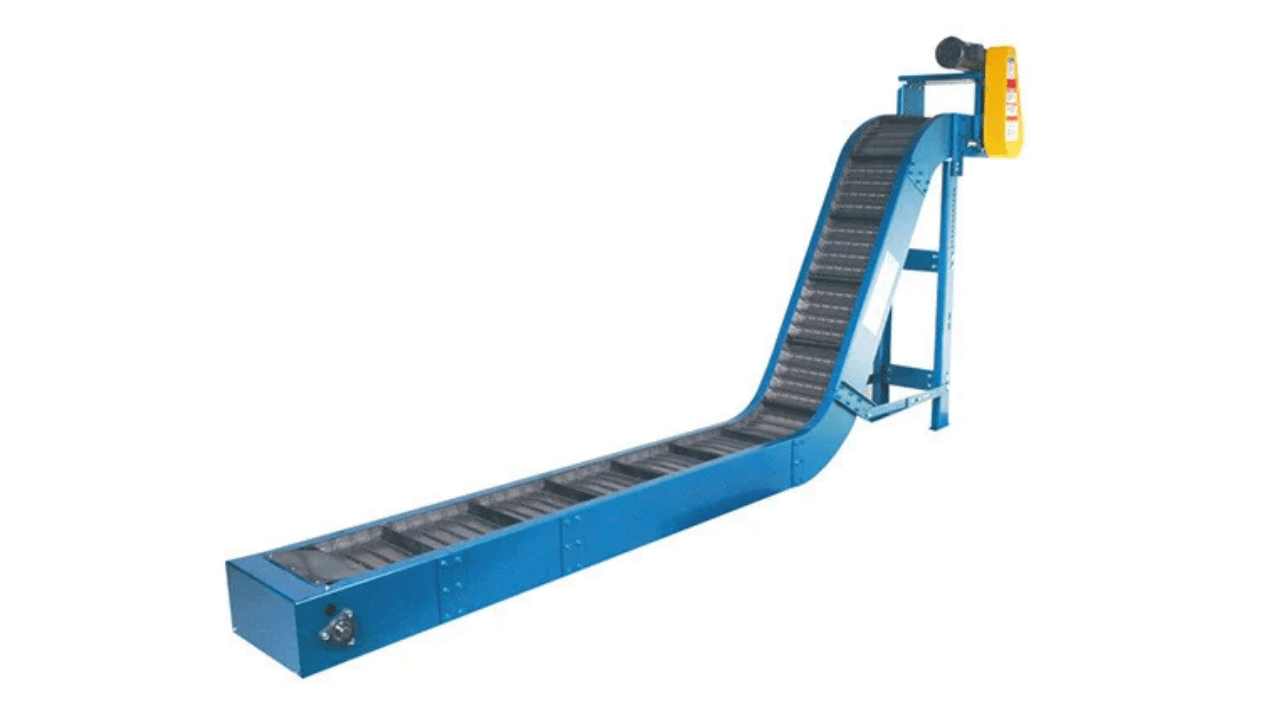

Chips can be removed quickly from the chip conveyors and trays, and buildup is avoided in order to maintain your machine’s performance. Debris collects in trays that are easily disposed of, and chips are removed from the cutting area and conveyed away. Keeping a workspace clean helps save downtime, protects machine components, and helps improve overall productivity.
Automation and Productivity Enhancements
16. Bar Feeders
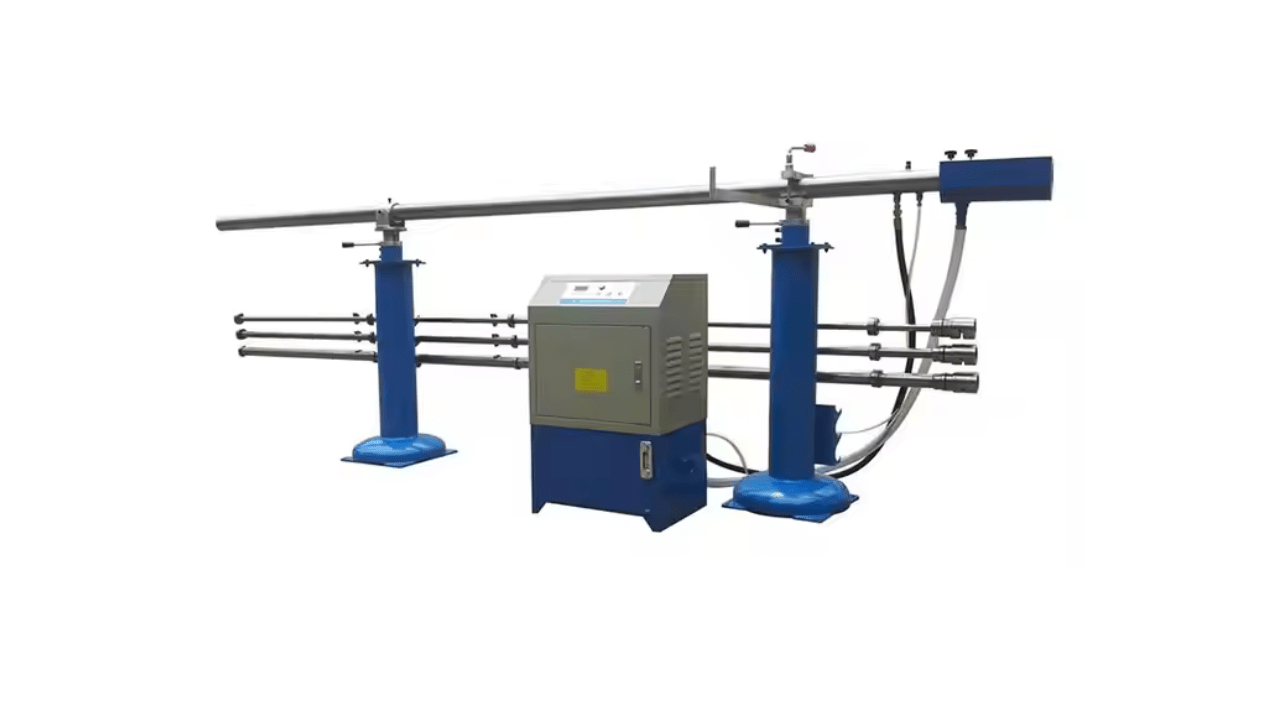

To load manually you still have to place raw material in front of your CNC lathe, but with bar feeders you can feed raw material automatically. It enhances efficiency, decreases downtime, and continues machining. This ultimately leads to consistent production, reduced operator intervention, and improved overall productivity.
17. Parts Catchers

Parts catchers allow you to collect finished workpieces so that they are not damaged and things are not unnecessarily handled by hand. This smooths things out even further, with their automated trays or bins keeping the parts safely in a holding position for further processing. A parts catcher increases efficiency, maintains quality, and increases production flow.
18. Robot Loader
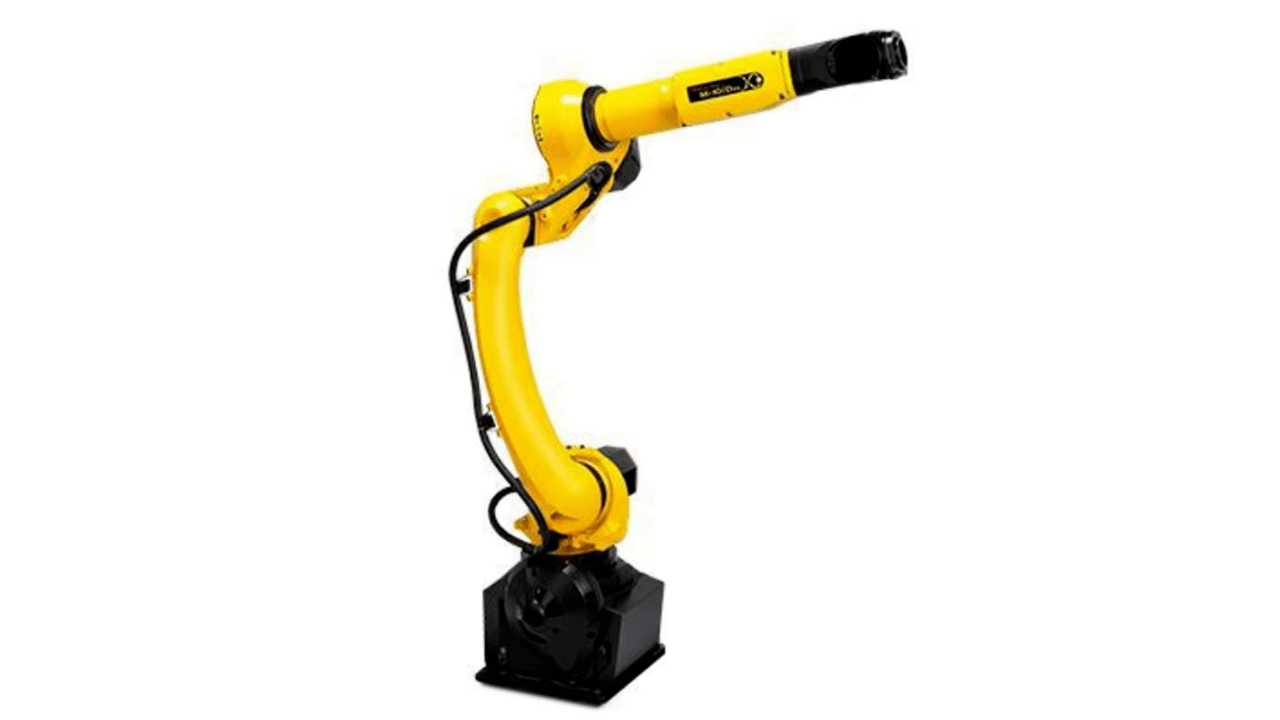

Robot loaders are used to load and unload material in order to save labor costs and to increase precision. Accurately handling them increases cycle time and consistency. The integration of robot loaders offers the opportunity to optimize workflow, minimize human errors, and build a highly efficient, automated machining environment.
Safety and Maintenance Accessories
19. Machine Guards and Enclosures
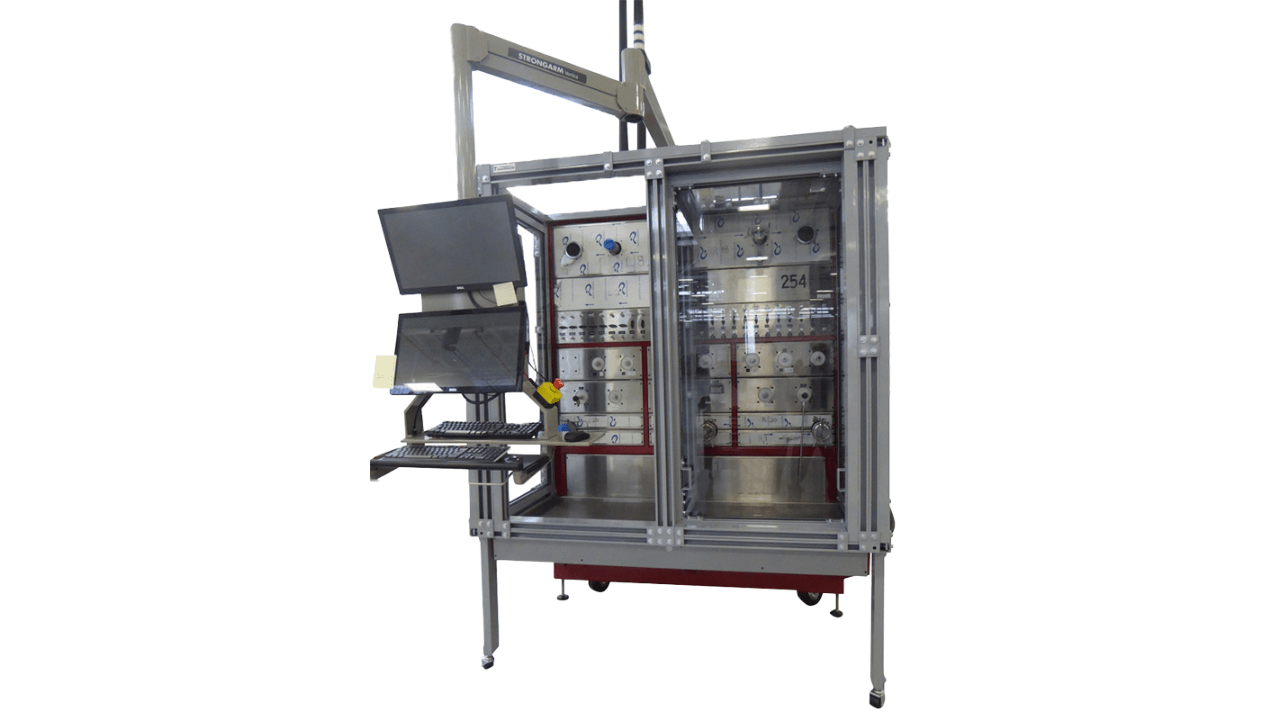

Machine guards and enclosures are used to protect your hands from flying debris, coolant splashes, and accidental contact with moving parts. These barriers act as barriers to the workplace safety and contain the noise and dust. Proper guards can reduce the chances for injury, meet the safety regulations, and help secure an entire machining area.
20. Chip Shields
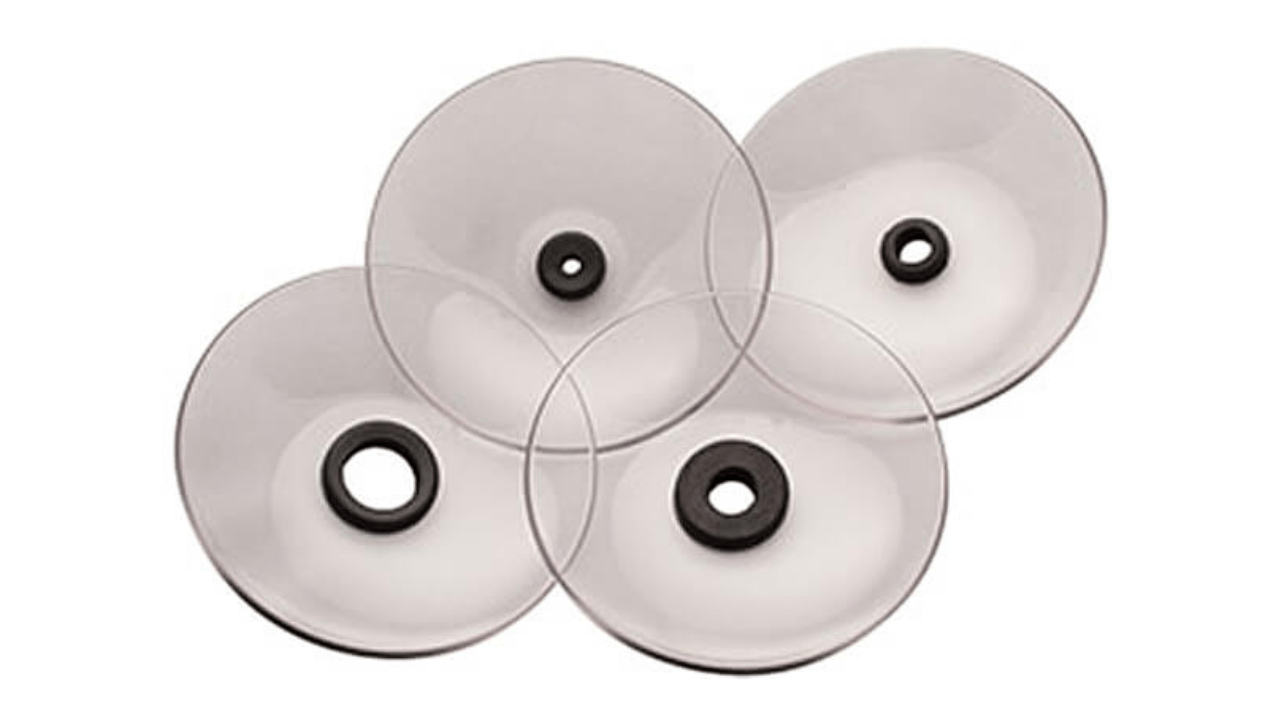

You use chip shields to keep the metal chips from getting to you or a machine component that is touchy. By replacing these barriers with transparent ones, the visibility is increased and the working space is cleaner and safer. Chip shields protect workers from injuries, lessen machine wear, and smooth out a machining process that is less dangerous and disruptive.
21. Maintenance Tools (Cleaning Kits, Alignment Tools)
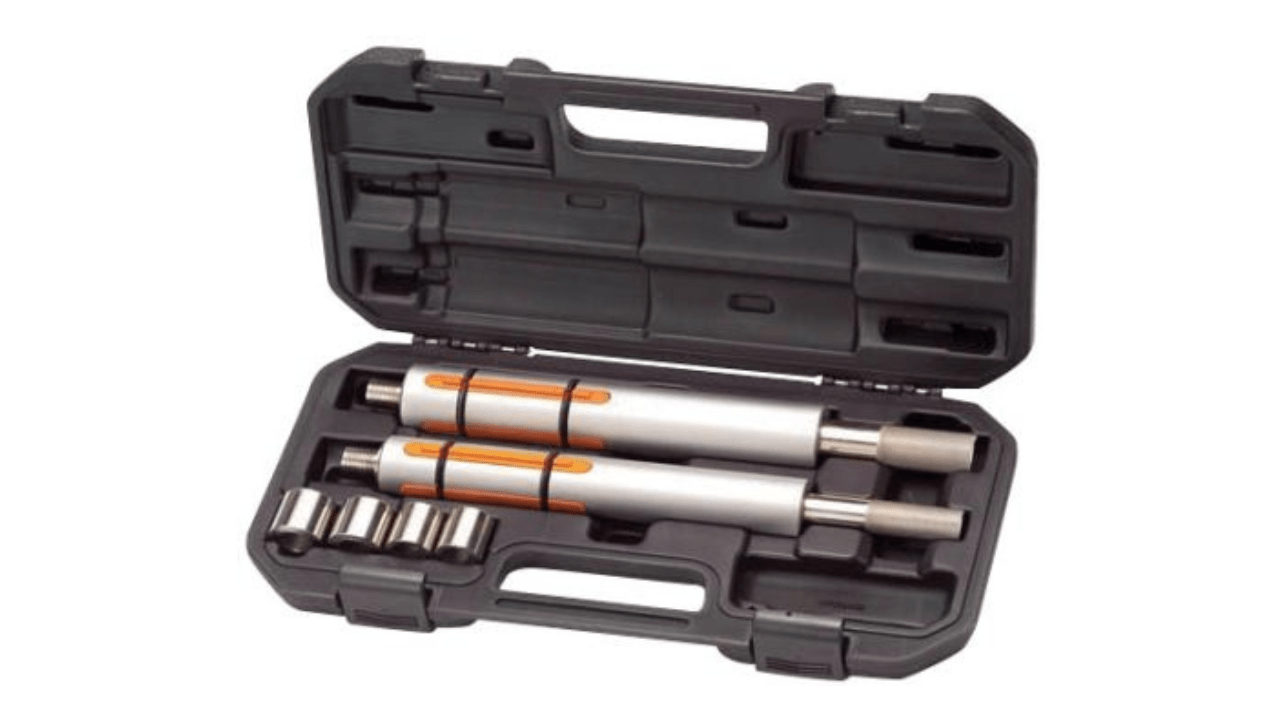

With a CNC lathe, you have cleaning kits and alignment tools to keep it in the condition it deserves as you leverage it for your projects. Brushes, scrapers, and lubricants are used to remove debris; precision alignment tools are used to align the machine correctly. Regular maintenance ensures the equipment is performing at its optimum and cuts down downtime and breakdowns and extends equipment life and therefore significantly reduces costs.
Conclusion
CNC lathe accessories are important as they help with precision, speed, and safety in machining. These tools provide consistency, improved work holding, tool holding, automation, and maintenance that enable each operation to perform at a higher quality, with less downtime.
More resources:
Lathe Machine – Source: TSINFA
Computer Numerical Control – Source: WIKIPEDIA


